11 min to read
Exploring Project Management Methodologies: Examples and Insights

The project management approach is a collection of tools and guidelines designed to facilitate effective and efficient project management. Broadly speaking, a particular project management style facilitates project management by providing a continuous sequence of tasks and principles. The main objectives of any such arrangement are to promote collaboration, improve efficiency, maintain budgets and improve the end result of the project.
How should you choose the right project management methodology?
Identify the essentials:
Start by gaining a basic understanding of the constraints and issues surrounding the project.
Identify factors critical to project success, allowing you to prioritise different aspects of the project. This prioritisation process will guide the selection of the project management style that aligns with your core objectives.
Comparative research should be done:
Gather a variety of project management strategies that can work within your resource availability and specific application constraints. Create a comparative analysis plan, focusing on the pros and cons of each business model in relation to your core variables and associated services and needs.
Take into account factors such as the approach’s adaptability to changes in project scope, risk management capabilities, and alignment with your team’s skills
Risk and Reward Management Analysis:
Use a comparison chart and project profile to assess the potential risks and benefits associated with each option. Be aware that the strategy with the highest potential for success may have increased risks.
Work closely with your project team, stakeholders and decision makers to assess acceptable levels of risk given the specific circumstances, objectives and constraints of your project.
Use insights from comparative analysis and risk analysis:
When considering how much risk can be tolerated, adopt the management style that is most aligned with the priorities of your project. Make sure your chosen approach is well communicated and understood by all team members and stakeholders.
Scrum methodology
Scrum
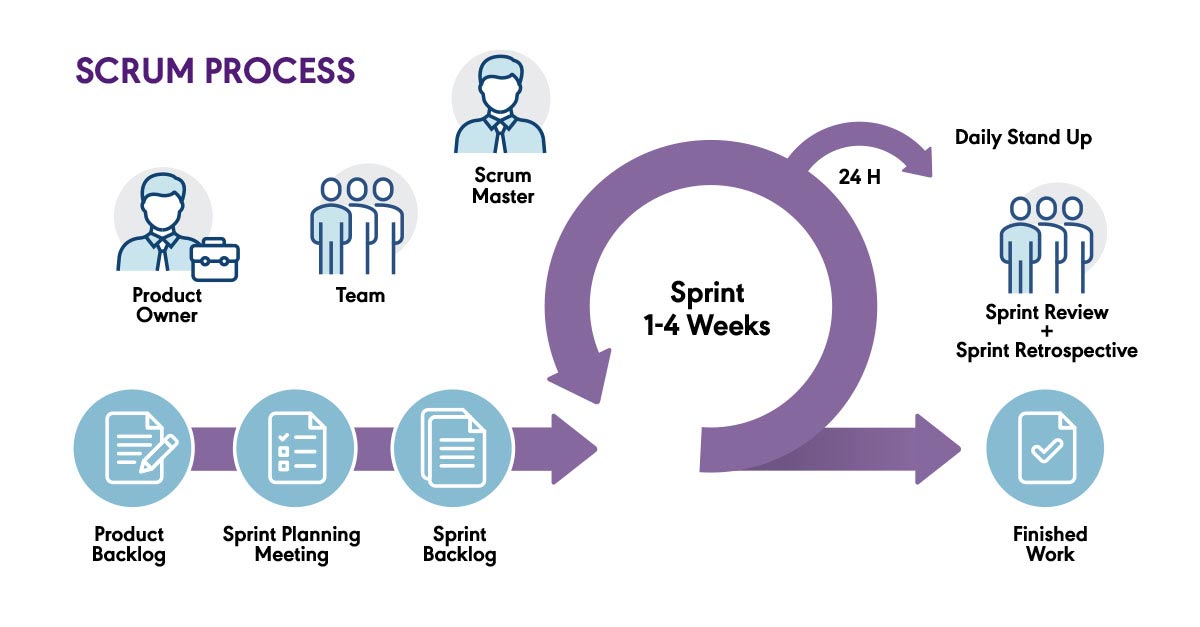
Scrum represents a project management approach that enables teams to swiftly, efficiently, and effectively adapt to change." It places a strong emphasis on achieving results by enhancing communication, collaboration, and development speed. This method underscores the importance of collaborative decision-making within the team and ensuring a consistent flow of valuable feedback to all involved stakeholders throughout the entire process.
Typically, Scrum is implemented when working in brief project phases known as "sprints." In this context, a team dedicates two to three weeks to attain a specific objective, subsequently regrouping to redefine the scope before commencing the subsequent phase. The Scrum methodology also revolves around delivering "shippable" portions of a project at periodic intervals during the process, rather than withholding results until the end of an extended timeline.
For example: The marketing team can plan and run campaigns using Scrum. They can run short, maybe a week or two.
Things like content creation, social media posts, email campaigns and website updates are completed in every sprint. Daily stations help team members coordinate their efforts and can quickly solve any problems. After each sprint, the team evaluates the campaign’s performance based on key metrics and adjusts its strategy accordingly.
Principles of Agility in the Context of Scrum Methodology
An agile methodology in business processes is a repeatable and flexible way to manage and deliver services. It emphasises collaboration, customer feedback, and the ability to meet changing needs throughout the lifecycle of a project. Agile methods are particularly well suited for projects where the scope and requirements must evolve or are not well defined at the outset. Here are some of the key principles and characteristics of the Agile methodology.
Iterative and Incremental Development: Agile projects are broken down into smaller increments or iterations, often called "sprints." Each run typically lasts two to four weeks and can be a high logistics load. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and incorporation of customer feedback.
Customer centricity: Agile has a strong focus on delivering value to the customer. Throughout the project, customers are encouraged to participate, and add their feedback to ensure that the product or service meets their needs and expectations.
Cross-functional teams: Agile teams are typically cross-functional, with different skill sets needed to complete a project. This can include developers, designers, testers and business analysts. The team members are cohesive and communicate regularly.
Embrace Change: Agile projects are designed to be flexible and scalable. They anticipate changes in requirements and can make changes to the project at any time, usually with little concern.
Continuous deliverables: Agile teams aim to deliver a high level of functional and releasable deliverables at the end of each sprint. This enables faster and more consistent delivery of value to stakeholders.
Example of agile methodology
Let’s consider a digital marketing agency running a marketing campaign for its e-commerce client. In this case, here is how they would collaborate with the Agile methodology
Initial Planning:
- The project manager collaborates with the e-commerce store to define the campaign objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- The team runs a backlog of marketing work, including social media content, email campaigns, paid advertising and a new website.
Sprint Schedule:
- The Scrum team (consisting of marketers, designers, product developers, and a Scrum Master) holds a sprint planning meeting to prioritise tasks and select items from the backlog for the upcoming sprint
- Then it’s the time to set goals such as increasing website traffic and increasing sales.
Sprint (repetitive):
- Marathons usually last two weeks. There are daily stand-up meetings, where team members discuss their progress, share insights and address any challenges. Marketers create and schedule social media posts, create ad compositions, write email campaigns, and optimise websites for conversions.
- Advertising performance and web analytics are constantly monitored to ensure alignment with campaign objectives.
- The team’s goal is to have a number of campaign items ready to use at the end of the race.
Sprint Review:
- At the end of the sprint, a sprint review meeting is held to present the campaign features and assess alignment with the client’s goals.
- The client provides feedback on all creative, messaging, and campaign operations.
- Changes are discussed and feedback is included in future runs.
Difference between Scrum and Agile
|
Aspect |
Scrum |
Agile |
|
Focus |
Communication, collaboration, and development speed |
Value delivery, customer-centricity, adaptability |
|
Decision-Making |
Collaborative decision-making within the team |
Collaborative decision-making within a flexible framework |
|
Feedback |
Consistent flow of valuable feedback to stakeholders |
Customer participation and feedback throughout the project |
|
Project Phases |
Structured into fixed-length phases (sprints) |
Iterative and incremental development, adaptable approach |
|
Sprint Duration |
Typically 2-3 weeks |
Varies based on project needs (e.g., shorter or longer) |
Kanban methodology
The Kanban method uses a visual tool called a "Kanban board" to represent a project backlog. Agile teams often use it to track project progress and resolve operational challenges.
Traditionally, kanban boards were made of physical objects such as a bulletin board or whiteboard. Digital tools are now used to create Kanban boards, allowing users to quickly move tasks from one stack to another as the team completes them.
Kanban is a highly flexible technique, allowing teams to tailor it to their specific needs. This flexibility also makes it a valuable partner for Agile.
The basic principles and elements of the Kanban method include:
Kanban boards: Kanban uses boards or visual systems to represent work items, tasks, or processes. These panels typically have columns representing different phases of the project (e.g., "To-Do," "In Progress," "Done"). Cards or tasks are moved in this list as the job progresses.
Workflow mapping: Kanban visualizes work elements, making it easier to see the status of tasks and identify bottlenecks or areas where work accumulates.
Work in Progress (WIP) Limits: Kanban places a limit on the number of tasks or work items allowed in each category. This prevents team members from becoming overwhelmed and helps the project run smoothly.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma revolves around increased quality assurance and consistency, alongside streamlining processes for greater efficiency. It is a data-driven project management approach that aims to eliminate inconsistencies and reduce waste. The Six Sigma method consists of a five-step cycle, blending composition and change to suit the needs of a growing business.
Six Sigma emphasises collective results over individual experience. The six sigma life cycle has five stages:
- Setting clear expectations.
- Performance analysis by measurement.
- Analyse and process information.
- Enhancing the process.
- Updates were implemented throughout the organisation.
The basic principles and elements of Six Sigma include:
DMAIC: This acronym stands for Teach, Learn, Evaluate, Improve, Control. DMAIC is a structured problem-solving method used in Six Sigma to identify, analyse, and eliminate inefficiencies and errors.
Data-Driven Decisions: Six Sigma relies heavily on data collection and analysis to make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement
Process mapping: This involves developing a detailed process map or flowchart to understand and document the existing process, so that improvement opportunities can be easily identified
Statistical tools: Six Sigma uses a wide variety of statistical tools and techniques to measure process performance, identify root causes, and evaluate improvement effectiveness
Successful implementation of Six Sigma requires a substantial initial investment by organisational leadership, including comprehensive training for all employees to successfully execute the phases of the cycle
Rapid Application Development(RAD)
Rapid Application Development, also known as RAD, is a dynamic software development model characterised by rapid adaptation, prototyping, and feedback, with little emphasis on detailed planning. Essentially, the RAD approach Takes development planning and prototyping takes much higher priority than performing a complete plan. Using rapid application development allows software developers to efficiently iterate and optimise software without having to start every step from scratch. This approach emphasises quality and contributes to results that are more in tune with end users’ needs.
RAD promotes ongoing user engagement throughout the development journey. Users are frequently integrated into the development team, offering constant feedback and insights. This guarantees that the ultimate product aligns with user requirements and anticipations, a particularly crucial aspect in enterprises where the software must accommodate intricate business operations.
Lean methodology
The Lean Project Management Methodology is centred around the principle of minimising waste and maximising efficiency in project management processes. It aims to streamline workflows, reduce unnecessary steps, and optimise resource utilisation to enhance project outcomes. In the context of Lean, "waste" refers to any activity or resource allocation that does not contribute value to the project. This methodology, often associated with practices initially popularised by organisations like Toyota, focuses on eliminating such waste to achieve leaner and more effective project management.
Here is a quick overview of how it works:
Define Value: Define what is valuable to the client or project stakeholders. This involves understanding the goals and needs of the project from the client’s perspective.
Value Stream Mapping: Create a detailed map or diagram of the entire project from inception to completion. This helps to identify all the steps and activities related to delivering value to the customers.
Eliminate Waste: Identify and eliminate any activities, positions, or resources that do not directly contribute to profitability. Program management includes frequent overproduction of various wastes, excessive paperwork, and unnecessary handouts.
Standardise and Simplify: Simplify and simplify the rest of the system to make it more efficient. This may include streamlining processes, automating repetitive tasks, or reducing unnecessary complexity.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
What is a project management methodology and why is it important?
A project management methodology is a set of guiding principles and processes used to plan, execute, and control projects effectively. It's crucial because it provides a structured framework that helps teams manage projects more efficiently, ensuring that tasks are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. By employing a methodology, organizations can minimize risks, maximize resource utilization, and achieve their objectives more predictably. It also facilitates better communication, collaboration, and accountability among team members, which are essential for the success of any project.
How can I choose the right project management methodology for my project?
Choosing the right project management methodology for your project involves considering several key factors, including the project's size, complexity, objectives, and the industry. It's also important to assess the team's expertise and the stakeholders' needs. For instance, Agile methodologies, like Scrum, are ideal for projects requiring flexibility and rapid iteration, commonly found in software development and digital marketing projects. For projects that are highly complex and where quality is paramount, a methodology like Six Sigma might be more appropriate. Assessing these factors will help you select a methodology that aligns with your project's goals and the working style of your team.
What are the key principles of the Scrum methodology?
The key principles of the Scrum methodology revolve around iterative development, team collaboration, and flexibility. Scrum emphasizes delivering products in short cycles called sprints, which allows for rapid feedback and continuous improvement. It promotes self-organizing teams that are empowered to make decisions, encourages daily communication through stand-up meetings, and focuses on delivering value to the customer. Transparency, inspection, and adaptation are fundamental principles, ensuring that progress is visible, challenges are addressed promptly, and changes can be incorporated seamlessly.
How does Scrum differ from traditional project management approaches?
Scrum differs from traditional project management approaches primarily in its flexibility, focus on teamwork, and iterative nature. Traditional methods, like the Waterfall model, are linear and sequential, where the project's scope, timeline, and costs are determined early on, and changes are difficult to implement. In contrast, Scrum is adaptive, allowing for changes and adjustments based on ongoing feedback. It emphasizes collaboration, with teams working in short sprints and constantly communicating to assess progress and obstacles. This makes Scrum particularly effective for projects in dynamic environments where requirements can evolve.
Can you explain the principles of agility within the Scrum methodology?
The principles of agility within the Scrum methodology include flexibility, speed, and responsiveness to change. Scrum embodies agility by organizing work in short, manageable sprints, enabling teams to quickly adapt to changes and deliver value incrementally. It prioritizes customer feedback, ensuring that the product meets users' needs and expectations. Agility in Scrum is also about continuous improvement, with regular retrospectives to reflect on successes and areas for enhancement. This approach helps teams become more efficient and effective over time, responding swiftly to market changes and new opportunities.
What is the Kanban methodology and how does it work?
The Kanban methodology is a visual project management system that emphasizes continuous delivery without overburdening the team members. It works by visualizing the workflow on a Kanban board, where tasks are represented as cards that move from left to right across columns, each representing a stage of the process. This method helps teams monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and manage workloads effectively. It encourages incremental changes to the existing process, minimizing disruptions while improving efficiency and throughput. Kanban is highly flexible and can be applied to various types of projects, making it popular in manufacturing, software development, and service delivery.
How can Six Sigma improve project outcomes?
Six Sigma can significantly improve project outcomes by reducing variability and defects in processes. It uses a data-driven approach and statistical tools to identify and eliminate causes of errors, ensuring that products or services meet quality standards. By focusing on process improvement, Six Sigma helps increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. It employs the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to systematically refine processes, leading to more predictable and improved project outcomes. Implementing Six Sigma can also foster a culture of continuous improvement within organizations.
What is Rapid Application Development (RAD), and when should it be used?
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is an agile software development methodology that emphasizes quick prototyping, iterative development, and the use of software tools to expedite the development process. It's particularly useful when the project scope is not fully known in advance and when speed is critical. RAD involves close collaboration between developers and end-users, ensuring that feedback is incorporated into the development process in real-time. This approach allows for rapid adjustments and helps ensure that the final product closely aligns with user needs. RAD is ideal for projects requiring fast delivery and where requirements are expected to change or evolve.
What are the core principles of the Lean project management methodology?
The core principles of the Lean project management methodology are centered on maximizing value and minimizing waste. This involves identifying and eliminating non-value-adding activities, optimizing processes, and ensuring that resources are used as efficiently as possible. Lean emphasizes delivering value to the customer, understanding customer needs deeply, and focusing efforts on activities that contribute directly to meeting those needs. Continuous improvement is a key principle, with teams always looking for ways to increase efficiency and effectiveness. Lean project management fosters a culture of collaboration, empowerment, and problem-solving, making it effective across various industries.
How do Scrum and Agile methodologies differ in their approach to project management?
Scrum and Agile are often used interchangeably, but they represent different concepts within the broader agile framework. Agile is a philosophy that encompasses a set of values and principles aimed at flexible, iterative development and a customer-centric approach to project management. Scrum, on the other hand, is a specific implementation of Agile that provides a structured method for applying these values and principles. It defines roles, events, and artifacts to guide teams in their agile journey. While all Scrum processes are Agile, not all Agile processes are Scrum. Agile methodologies can include other frameworks like Kanban or Lean, each with its unique practices and emphasis, offering flexibility in applying Agile principles to various project types and environments.

About Bruno GavinoBruno Gavino is the CEO and partner of Codedesign, a digital marketing agency with a strong international presence. Based in Lisbon, Portugal, with offices in Boston, Singapore, and Manchester (UK) Codedesign has been recognized as one of the top interactive agencies and eCommerce agencies. Awarded Top B2B Company in Europe and Top B2C company in retail, Codedesign aims to foster personal relationships with clients and create a positive work environment for its team. He emphasizes the need for digital agencies to focus on data optimization and performance to meet the increasingly results-driven demands of clients. His experience in digital marketing, combined with a unique background that includes engineering and data, contributes to his effective and multifaceted leadership style. |

About CodedesignCodedesign is a digital marketing agency with a strong multicultural and international presence, offering expert services in digital marketing. Our digital agency in Lisbon, Boston, and Manchester enables us to provide market-ready strategies that suit a wide range of clients across the globe (both B2B and B2C). We specialize in creating impactful online experiences, focusing on making your digital presence strong and efficient. Our approach is straightforward and effective, ensuring that every client receives a personalized service that truly meets their needs. Our digital agency is committed to using the latest data and technology to help your business stand out. Whether you're looking to increase your online visibility, connect better with your audience, get more leads, or grow your online sales. For more information, read our Digital Strategy Blog or to start your journey with us, please feel free to contact us. |
CodeDesign is leading:
- Digital Agency
- Digital Marketing Agency
- Digital Ecommerce Agency
- Amazon Marketing Agency

Add comment ×